For this EdTech Inquiry, Cheyenne and I have chosen to investigate, “what are some technologies that can help students with learning difficulties?“
We chose this topic because we are passionate about special education and thought it would be helpful as future educators to know more about the different types of assistive technologies than can be used to support diverse learners. To better explain these various technologies, we decided to organise them by learning difficulty.
Before we begin, please watch the following video that discusses how using technologies helps to support diverse learning needs, Using Technologies to Support Diverse Learning Needs. The video highlights the importance of using technology to assist students in the classroom to ensure their academic success. It is important to incorporate different technologies in the classroom to ensure that learning is accessible to all. This provides an inclusive learning environment. Now, we will discuss the different possible assistive technologies…
Autism:
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disability that can cause significant social, communication and behavioural challenges. For students with ASD, assistive technology can be used to support and enhance communication in the classroom.
Some great assistive technologies include:
- Tobii Dynavox – This technology is great for students with Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified (PDDNOS) and Rett Syndrome, both of which fall under the Autism Spectrum. This device is beneficial for these students, who are often non-verbal and experience significant mobility issues. Tobii Dynavox is a speech-generating device that is controlled by eye movement and gaze.
For more information on how Tobii Dynavox works, view this video below:
2. Proloquo & TouchChat – These two programs are used to help non-verbal students with their communications skills and provide them with a “voice”. These programs can be downloaded directly to students’ iPads or phones and be used to help them communicate in any place, at any time. The video below provides a brief overview of how TouchChat and Proloquo are used.
3. ChoiceWorks – This app is great for students who struggle with transitions! It has a built in visual schedule and a timer, to show kids exactly how much time is left before they are expected to move onto the next activity. The view below provides an in-depth tutorial of how ChoiceWorks is used.
ADHD:
Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder is a condition that can cause individuals to experience unusual levels of hyperactivity and engage in impulsive behaviours. Students with ADHD may also have trouble focusing their attention on a single task or sitting still for long periods of time. In addition to this, students with ADHD may benefit from a wide variety of assistive technologies. The following list of assistive technologies below can be utilised to assist students with ADHD in the classroom.
- Audio books/reading software – An assistive technology that reads the book aloud to the reader.
- Screen readers – A screen reader will read the text and images on a computer and output the information to the user by speech or braille
- Digital typewriter – For students that require some assistance with writing and fine motor skills, a digital typewriter is a helpful tool. A digital typewriter allows students to type on a keyboard, which can then be transferred to a computer.
- Dictation/speech-to-text – This assistive technology is very user friendly and helpful for students that require support with their writing and fine motor skills. With dictation, the user must simply speak into the microphone on the computer and text will appear on the screen. So, instead of typing, the user will speak and text will generate i.e. speech-to-text. (full description in Dysgraphia)
- Word prediction software – The name of this assistive technology describes its function, as it predicts the next word that you will type. This is helpful for students with dysgraphia as it limits the amount of typing required. One drawback of word prediction softwares is that if a student does not understand the word that is predicted, then it can cause the student to write a text that is misunderstood. However, the benefits of this software outweigh the cons as it is a great assistive technology for students to use while typing.
Dysgraphia:
Dysgraphia is a disorder of written expression that impairs an individual’s writing ability and fine motor skills.
Some great assistive technologies include:
- Dictation/speech-to-text – This assistive technology is very user friendly and helpful for students that require support with their writing and fine motor skills. With dictation, the user must simply speak into the microphone on the computer and text will appear on the screen. So, instead of typing, the user will speak and text will generate i.e. speech-to-text.
Some applications that you can download for the speech-to-text software can be found using the following links:
Speechnotes – Speech To Text Notepad – Apps on Google Play
Dictation – Speech to text on the App Store (apple.com)
Please watch the example video below of me using the dictate function on Microsoft Word:
- Digital typewriter – For students that require some assistance with writing and fine motor skills, a digital typewriter is a helpful tool. A digital typewriter allows students to type on a keyboard, which can then be transferred to a computer. One drawback of digital typewriters is that some models can be fairly expensive. Please follow this link to view a wide variety of different digital typewriters, Amazon.ca : digital typewriter.
- Word prediction software – The name of this assistive technology describes its function, as it predicts the next word that you will type. This is helpful for students with dysgraphia as it limits the amount of typing required. One drawback of word prediction softwares is that if a student does not understand the word that is predicted, then it can cause the student to write a text that is misunderstood. However, the benefits of this software outweigh the cons as it is a great assistive technology for students to use while typing.
Dyslexia:
Dyslexia is a learning disorder in which individuals experience difficulties with accurate and/or fluent word recognition, poor spelling, and decoding abilities.
For students with Dyslexia, many of the same technologies used for those with Dysgraphia can be beneficial.
- Dictation/Speech-to-text
- Word Prediction Software/ Spell Check
- Screen Readers
Hearing Impairment:
Hearing impairment, deafness, or hearing loss refers to the total or partial inability to hear sounds. For students with any form of hearing impairment, some assistive technologies include:
- Closed Captions – This is an assistive technology that can be added to television and online video platforms, such as YouTube. Closed Captions provide the viewer with text transcription of the audio, making it easier for them to understand what is being said. Please watch this video that we created using closed captions:
- Microphone and speaker System – The microphone is worn by the teacher to help project their voice through a series of speakers throughout the room. These systems can also be wireless connected via bluetooth to students’ hearing aids. A great example is Front Row.
Visual Impairment:
Visual impairment, blindness, or visual loss refer to the total or partial inability to see. For students with any form of visual impairment, some assistive technologies include:
- Alt-Text – This is an assistive technology that is accessible to all and should be used whenever an image is used for information (not decorative). As I have previously mentioned in another blog post on week 7, “good alt-text description is specific, brief, and less than 125 characters”. Alt-text must be used on images, otherwise screen readers will be unable to describe the image to the user. Please visit this website as it provides a helpful description on creating a beneficial alt-text description, How to write better alt-text descriptions for accessibility – The Big Hack.
- Described Video – Described video is an essential assistive technology for individuals with visual impairment, blindness, or vision loss as it provides information on the visual media of a video. With described video, the visual media of a video are auditorily described to the viewer. The full description of describe video is as follows:
“Described Video (DV) uses a secondary audio track synchronized with media to provide aural representation of visual narrative of a program’s non-verbal elements that may include surroundings, costumes and body language. The description is added during pauses in dialogue, and enables people to form a mental picture of what is happening in the program.” (Post Production Described Video (DV) | Accessible Media Inc. (ami.ca))
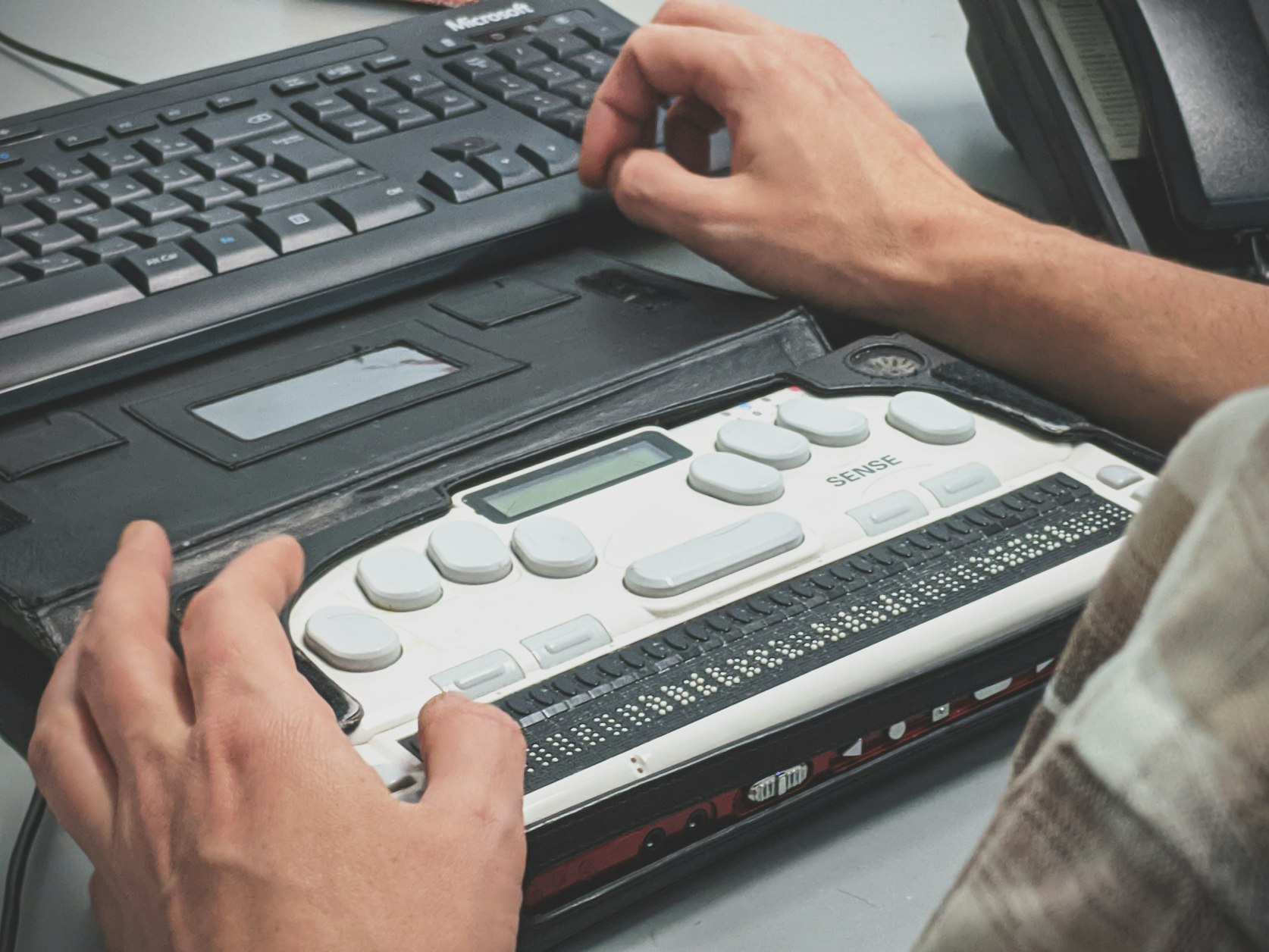
- Screen Readers – A screen reader will read the text and images on a computer and output the information to the user by speech or braille. This assistive technology is essential for individuals with visual impairment, blindness, or vision loss to access technology. Screen readers will read all the information on the screen, which is why it is important for individuals to create meaningful and specific alt-text descriptions on their images. Otherwise, the user will be unable to determine the importance and context of the image.
In conclusion, assistive technology is a requirement to ensure that content and information is accessible and inclusive to all. As we have discussed, assistive technology can be implemented in a wide variety of ways depending on the learning difficulty of the user. As future teachers, we see the benefit of understanding and implementing assistive technology in the classroom. We hope that with this inquiry other educators will feel confident in their ability to implement assistive technology in the classroom and choose which is best suited for their diverse learners.
Disclaimer: This is not an exhaustive list! There are thousands of various technologies, apps, programs, etc. that can be used to improve student success in the classroom! These are just some of the few resources we found during our research 🙂